

You can configure changing the header name from the CLI. This can be useful if you want to use a custom header name instead of the standard header name. If you select preserve client IP from the web-based manager or enable the http-ip-header option from the CLI you can also change the name of the X-Forwarded-For header to a custom header name. P r ese r v i n g the client IP address but changing the X-Forwarded-For header name If this option is not selected, the header will contain the IP address of the FortiGate unit.
This can be useful in an HTTP multiplexing configuration if you want log messages on the real servers to the client’s original IP address. Select preserve client IP from the web-based manager or enable the http-ip-header option from the CLI to preserve the IP address of the client in the X-Forwarded-For HTTP header. To enable HTTP multiplexing from the CLI enable the http-multiplex option. To enable HTTP multiplexing from the web-based manager, select multiplex HTTP requests/responses over a single TCP connection. However, in most cases HTTP multiplexing should only be used if enabling it leads to a measurable improvement in performance. HTTP multiplexing can also improve performance between a web server and the FortiGate unit if the FortiGate unit is performing SSL acceleration. For example, if users web browsers are only compatible with HTTP 1.0. HTTP multiplexing may improve performance in some cases. This may reduce the load on the backend server and increase the overall performance. HTTP multiplexing can take multiple separate inbound sessions and multiplex them over the same internal session. The result is fewer idle sessions on the web server so server resources are used more efficiently. This allows a single HTTPD process on the server to interleave and serve multiple requests.

HTTP multiplexing is a performance saving feature of HTTP/1.1 compliant web servers that provides the ability to pipeline many unrelated HTTP or HTTPS requests on the same connection. You can also configure load balancing to offload SSL processing for HTTPS and SSL traffic.įor both HTTP and HTTPS load balancing you can multiplex HTTP requests and responses over a single TCP connection. Similarly for HTTPS load balancing, set the virtual server type to HTTPS and then select the interface, virtual server IP, and virtual server port that matches the HTTPS traffic to be load balanced. The default virtual server port for HTTP load balancing is 80, but you can change this to any port number. The virtual server will load balance HTTP sessions received at the virtual server interface with destination IP address that matches the configured virtual server IP and destination port number that matches the configured virtual server port. In a firewall load balancing virtual server configuration, you can select HTTP to load balance only HTTP sessions.
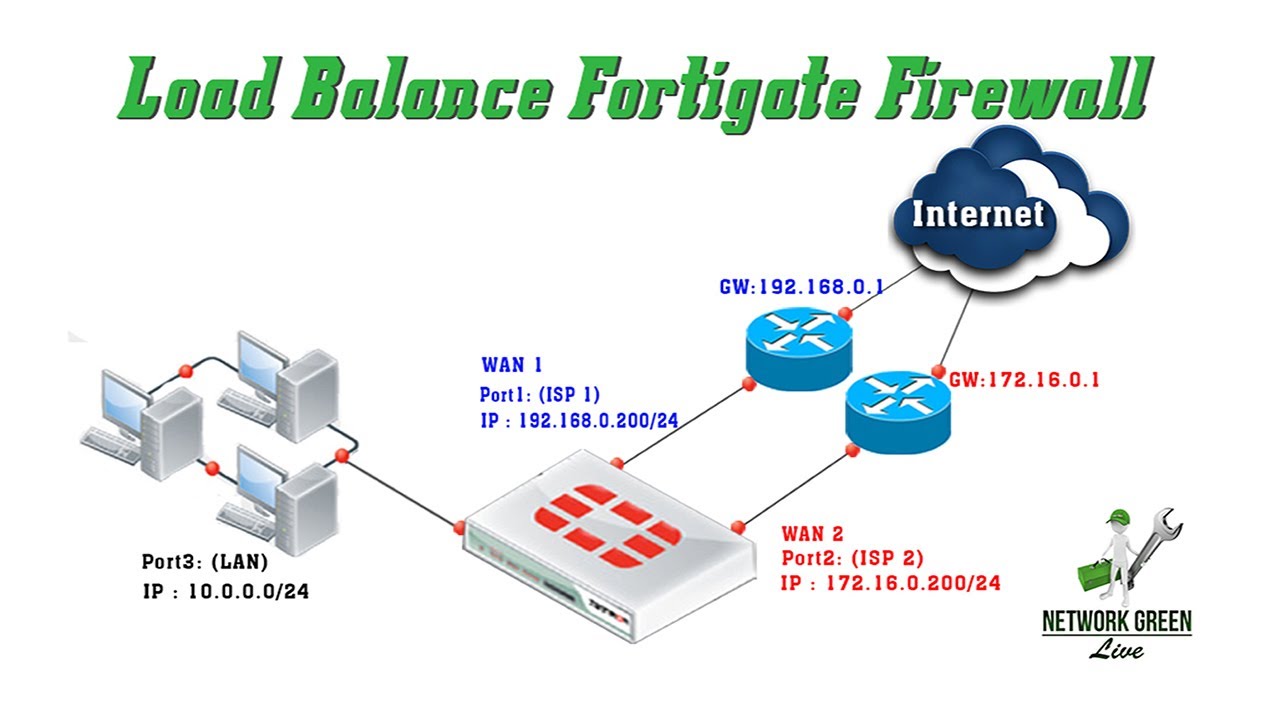
H TT P and HTTPS load balancing, multiplexing, and persistence


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
